Canada is one of the most beautiful countries in the North America continent. Its attractive natural landscapes and incredible scenery render it the best place to visit. Canada is also well renowned for its excellent education system that attracts millions of international students from different parts of the world every year.
The Canadian government prioritizes education more than many countries.. It boasts a well-established public education system funded, administered, and run by the federal and provincial governments. The Canadian provinces and territories oversee the jurisdiction of Canada’s public education system, including the curriculum.
Quality of Education in Canada
Canada, home to some of the best educational institutions, offers quality education right from pre-elementary all the way to graduate studies. According to the latest report by the US News, Canada ranked 3rd best country in quality of education.
Education is mandatory in every Canadian province up to the age of 16, except in Ontario and New Brunswick provinces, where the compulsory age is 18. About 90 per cent of Canadians have at least high school diplomas.
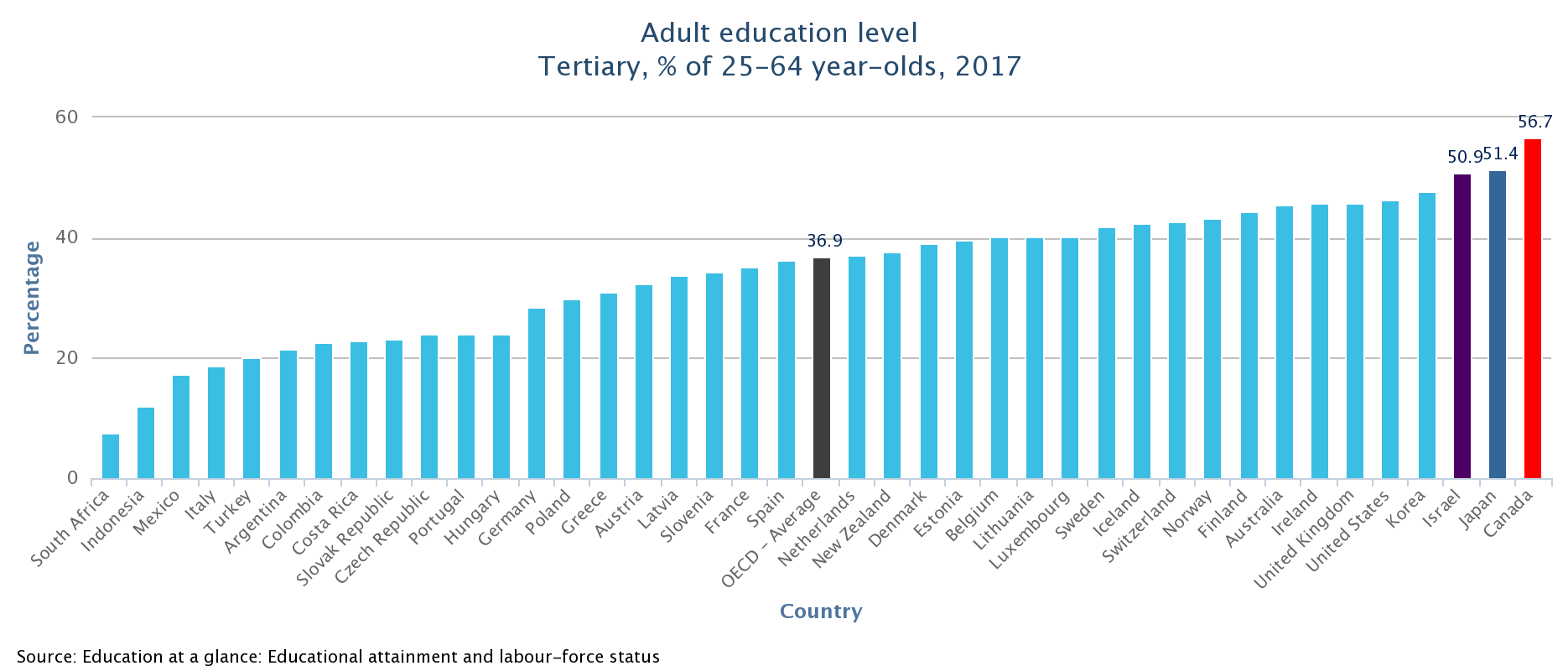
Studies show that Canada ranked as OECD’s (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development) most educated country. About 56.7 per cent of Canadian adults have received a post-secondary degree. That is 10 percent higher than the United States.
Structure of Education in Canada
Various education options are available in Canada, rendering it one of the most popular destinations for students from other parts of the world. Here are the education levels we’ll discuss.
- Pre-elementary education
- Elementary (primary) education
- Secondary school education
- Post-secondary education
- Graduate Education (Masters and Doctoral)
Canada also offers high-quality language education to most international students. You can improve your French and English language skills by enrolling in a language school. Also available are vocational schools which offer career-focused education.
1. Pre-Elementary Education in Canada
Pre-elementary schools in Canada offer education programs to children who are below six years. They include daycare schools for toddlers and kindergartens for children who are 4-5 years old. Most federal, private, and public schools provide pre-elementary education.
Most Canadian provinces offer jurisdictions of a one-year pre-elementary education in the public schools (kindergarten). However, regions like Alberta, Ontario, Saskatchewan, Quebec, and Manitoba provide additional years of free pre-elementary learning.
In Quebec, an additional year of free pre-elementary learning is available to four-year-old kids who are coming from low-income families or are disabled. In Ontario, it’s the school board that decides whether a child should receive the free additional year or not.
Usually, kindergarten education (learning program in the year before elementary school) in most jurisdictions is available to kids turning five at a date specified in the legislation. Some jurisdictions offer half-day kindergarten programs while others provide full-day.
Pre-elementary education in Canada is designed to prepare kids for elementary (primary) school. Children get an opportunity to learn the alphabet, mathematics skills, pre-reading skills, art, and music. They also learn how to relate with people surrounding them.
2. Elementary (Primary) Education in Canada
All children must enroll in an elementary school once they complete pre-elementary education. Each Canadian province or territory has a legal right to decide when the school year should start or end. In many cases, it usually begins in September and ends in June.
Most children begin their elementary education at the age of six or seven in Grade one. Primary education is a six-year program that runs from Grade one to Grade six. However, some schools offer elementary education up to Grade 8.
Here are the Grades of elementary education based on age classes.
| Education Level | Age Bracket (Years) |
| Grade 1 | 6 – 7 |
| Grade 2 | 7 – 8 |
| Grade 3 | 8 – 9 |
| Grade 4 | 9 – 10 |
| Grade 5 | 10 – 11 |
| Grade 6 | 11 – 12 |
The curriculum for primary education varies by province. But it generally comprises of subjects such as reading and writing courses, mathematics, geography, science, music, art, history, and physical education. French is a compulsory subject in some provinces.
Promotion from one grade to another is performance-based. Students must pass the end school year exams to proceed to another Grade. Children who perform poorly can be held back to repeat. Students with incredible academic performance may skip a Grade entirely.
When it comes to the costs of education, elementary education in public schools is free for Canadian residents. However, some schools may charge a small fee for children to take part in extracurricular activities like sports and school trips.
Private elementary schools in Canada charge fees, and they must provide the same curriculum as the public schools. That promotes fairness and ensures that every student completes the approved curriculum that children in public schools study.
3. Secondary Education in Canada
When children complete primary education, they enroll in secondary education, which consists of an intermediate (junior high) school and a high school.
Junior High School (Intermediate School)
When students complete their elementary education at Grade 6, they move to a junior high school (intermediate level). The intermediate level consists of two Grades. Grade 7 for children aged 12 – 13 and Grade 8 for children aged 13 – 14.
At Grade 7, students attend different classes in a day with different teachers tutoring them every day. Every subject has its teacher, who is an expert in that particular area of study. All teachers must have certificates that show they are experts in the subjects they teach.
Intermediate schools may continue teaching students the core units they learned in primary schools, although at advanced levels. The primary objective of the intermediate level is to prepare students for high school education.
High School Education
High schools consist of a four-year program that runs from Grade 9 to Grade 12. The table below shows the Grades in high school education by age.
| Education Level | Age Bracket (Years) |
| Grade 9 | 14 – 15 |
| Grade 10 | 15 – 16 |
| Grade 11 | 16 – 17 |
| Grade 12 | 17 – 18 |
In Ontario, students can study in high school for up to the 5th year, also known as Grade 12+. In Quebec Province, secondary education proceeds up to Grade 11, then followed by a two-year college (pre-university) and a three-year university education.
Most high schools often divide students into separate academic classes. That gives each student the chance to focus on subjects that are more specific to what they are interested in studying in the university or college. The subjects can influence their lifetime careers.
Even when dividing students into different streams based on subject choices, there are some compulsory subjects that all students must study apart from the elective subjects. Some of them include sciences, physical education, mathematics, English, and health.
High schools also offer career guidance and counseling to students. That helps learners to select the right elective subjects that will land them onto their career paths. Counselors are present in schools all the time to help students plan for post-secondary education.
4. Post-Secondary Education in Canada
When students graduate from high school, they can enroll in post-secondary education, which can be either a college or a university. Post-secondary education is a career-focused type of learning that builds the students’ practical skills they can apply in various workplaces.
Upon completing high school, students can select any college or university of their choice depending on their fields of study. While most people may think that college and university mean the same thing, they are two different institutions with different education.
What is a College Education in Canada?
A college is typically smaller than a university when it comes to the size differences. In Canada, most people look at colleges as educational institutions that offer applied arts, technical, and applied sciences. Some people also refer to schools with short courses as colleges.
In general, many colleges in Canada offer diplomas, vocational certificates, and associate degrees. Some colleges offer undergraduate degrees as their highest level of education. Notably, career colleges and community colleges are the most popular in Canada.
Many students in Canada join colleges to prepare for university education. It allows them to gain transferable credits they can apply to university once they move. Other students also study in colleges to enter the job market once they finish their studies.
What is University Education in Canada?
A university is a higher learning institution that offers both undergraduate and graduate degree programs in various fields of study. Unlike colleges, universities provide a vast range of degrees, including a bachelor’s degree, master’s degree, and a doctoral degree.
- Bachelor’s Degree: Also referred to as an undergraduate degree, this program takes about 3-5 years for full-time students in Canada to complete
- Master’s Degree: It’s a more specialized degree that takes two years for full-time Canadian students to complete. Master’s degrees involve a lot of research work.
- Doctoral Degree (Ph.D.): It’s the most specialized and highest level of academic degree in Canada. Doctoral degrees in Canada take around 3 – 6 years to finish.
Costs of Post-Secondary Education (Undergraduate Studies) in Canada
It is no secret that the prices of post-secondary education in Canada have been rising steadily for the past few years. In a report by Canada Statistics, Canadian students pay an average tuition fee of CA$6,838 per year for an undergraduate program.
Besides paying for tuition fees, Canadian students must also budget for related education expenses such as accommodation, food, and books. Since post-secondary education is expensive, programs like RESPs can help students pay for their tuition fees.
How RESPs Work in Canada
An RESP is a registered education savings plan that Canadian parents use to save for their children’s post-secondary education. Upon opening an RESP account, parents must contribute money into the account periodically. Most parents make monthly contributions.
As a government-sponsored initiative, RESP comes with numerous incentives, including tax-free growth of parents’ investment. The government also offers the Canada Education Savings Grant (CESG) of 20 percent of every contribution up to CA$2,500 per year.
Beneficiaries can get a maximum CESG of CA$500 every year if their parents contribute at least CA$2,500 into the RESP accounts. Low-income families in Canada are eligible for additional grants from the government besides the CA$500 CESG.
When the beneficiaries join a college or university, the government disburse the funds into their accounts in the form of Educational Assistance Payments (EAPs). The student should only use the money to finance their tuition fees and related expenses.
It’s no secret that RESPs have helped many Canadian parents to finance their children’s post-secondary education. You can learn more about RESP by reading A Knowledge First Financial Review on What Are RESPs.
5. Graduate Education in Canada
Canada is home to some of the top universities that provide the best graduate education in the world. That has made the country lead globally in research and innovation. Canada has a long history of coming up with novel innovations.
Typically, graduate education in Canada comprises of the master’s degree and doctoral degree. As mentioned earlier, a master’s degree takes two years, while a doctoral degree takes between three and six years to complete.
Graduate education is different from undergraduate education. Characterized by a focused, advanced, and scholarly learning environment, graduate education emphasizes on acquisition and application of qualitative research skills.
In Canada, graduate education can be categorized further into professional, terminal, and non-terminal programs. Professional programs offer specialized training for a particular profession. In terminal programs, the master’s and doctoral degrees have no link to each other. In a non-terminal program, a master’s degree leads directly to a doctoral degree.
Conclusion
With its well-established education system, Canada offers world-class education, right from pre-elementary schools to post-secondary schools and graduate schools. Children studying in Canada receive quality education because their teachers are well-trained.
Most schools in Canada also have a plethora of extracurricular activities to make learning more enjoyable. Students can participate in sports activities like hockey, football, and gymnastics. They can also take part in cultural activities like photography, arts, and choir. The education system is designed to build the students’ knowledge and practical skills.
You Might Want To Read:
Ukpsc Acf Assistant Conservator Of Forest Online Mock Test, Isc Xii Commerce Practice Test, Hopes Academy, Motion Mtse Motion Talent Search Examination Class 11Th, Cat Quantitative Aptitude Sample Paper With Solutions Set 07, Jee Main Advanced Physics Circular Motion Part 2, Upsc Mains 2018, Ugc Net Russian Syllabus 2017 Code 41, Bitsat 2017 Major Online Test Series Pcm Formulae Handbook Set Of 3 Books By Career Point, Vizag
Leave your vote
This post was created with our nice and easy submission form. Create your post!